UFR ( Urine Full Report ) is a test generally carried out at all clinical laboratories. It’s also known as urine analysis. It’s used to screen or diagnose substances or cellular materials in urine associated with metabolic disorders, renal function and urinary tract infection ( UTI ).
UFR mainly includes three main examinations.
- Physical / macroscopic examination
- Chemical examination
- Microscopic examination
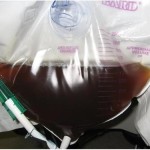
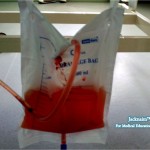
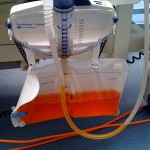
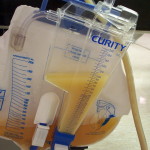
In physical examination, the color, the appearance and the odor of the urine are considered. In most of the circumstances, the patient’s health status can be predicted with color of the urine. A healthy individual’s urine is normally shade of yellow. It ranges from pale yellow to yellow depending on the concentration of solutes in ( pH ) urine and pigments. Urochrome, uroerythrin and urobilin are pigments reason for the characteristic color of urine.The acid urine is darker than alkaline urine.
Many constituents and factors can alter the normal color of urine. It includes diets, drugs and disease. Abnormal colors of urine include green, brown, red, orange and milky. Reasons for abnormal colors are explained below.
I. Green 
- Drugs: Cimetidine, Promethazine, Amitriptyline, Flutamide, Indomethacin, Methocarbamol, Mitoxantrone, Propofol, Phenylbutazone, Triamterene
- Disease: Bacterial infection,Hartnup Disease, Indicanemia, Indicanuria
- Dyes: Carbolic Acid, Flavine derivatives, Indigo Blue, Methylene Blue, Resorcinol
II. Brown
- Brown / Tea color :-
- Drugs: Lvadopa, nitrofurantoin, metronidazole
- Condition: Rhabdomyolosis (myoglobinuria), bile pigment
- Other: Fava beans
- Dark yellow
- Condition: Fever , dehydration
-
Black brown:
- Drugs: Stimulant laxatives (e.g. cascara, senna)
- Condition: Alkaptonuria, methemoglobinuria
- Other: Melanin
III. RED
- Drugs: Levadopa, nitrofurantoin, metronidazole
- Condition: Rhabdomyolosis (myoglobinuria), bile pigment,Kidney Stones, Malignancy, Trauma, Infection (Pyelonephritis, UTI, pyonephrosis, cystitis, prostatitis, TB, schistosomiasis)
- Other: Fava beans
IV. Orange
Drugs: Idarubicin, Ferrioxamine, Oxamniquine, Phenazopyridine, Rifampicin, Sulfasalazine, Warfarin
Food/supplements: Carotenes, B-complex vitamins, Senna, Rhubarb, Beets and blackberries Condition (hypercarotenemia): Diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypothyroidism, porphyria
V. Milky
Condition: Phosphaturia ( Amorphous urate, amorphous phosphate ), Urinari tract infaction (UTI)
References: