HDN is caused by hyper immune IgG immunoglobulin during pregnancy. The hyper immune immunoglobulins are able to cross the placenta and bind with corresponding antigens on the surface of fetal RBC. Eventually this will lead to hemolysis of fetal RBC. This is also called as Erythroblastosis fetalis.
There are two instances where hyper immune immunoglobulins (IgG) are developed.
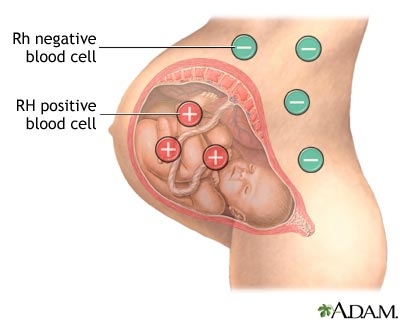
1. When Rh negative mother conceiving Rh positive baby.
2. When blood group O or group A2 mothers conceiving blood group A, B and AB baby.
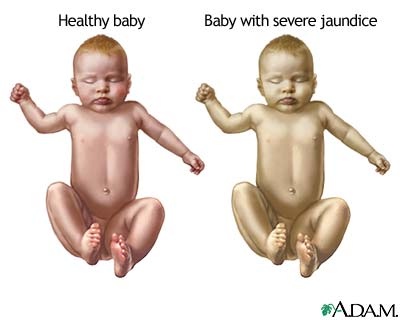
When the fetal RBCs enter to the mother’s circulation during pregnancy or delivery, mother becomes sensitized to them. The mother produces hyper immune immunoglobulin – IgG against fetal RBCs. These immunoglobulins are able to cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs. Therefore the neonate is likely to have anaemia, hepatosplenomegaly and jaundice.
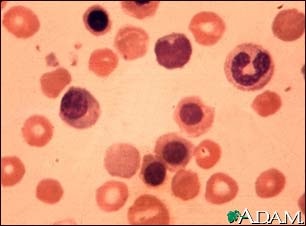
The condition is diagnosed by a blood film of newborn and HbF staining of mother’s blood film. The newborn blood film shows spherocytes and polychromasia with various immature stages of RBC especially normoblast.
The treatment to HDN depends on the severity of condition including temperature stabilization, phototherapy and exchange transfusion.
Hyper immune immunoglobulins are managed in mother’s circulation by giving anti D immunoglobulins – rhogum to mother 24 th week of gestation and immediately after delivery in the purpose of neutralizing all Rh positive cells. The rhogum is given to Rh negative mother within 72 hours after delivery. After 72 hours, mother is sensitized to Rh positive cells.
Photo credits: http://health.allrefer.com/health/newborn-jaundice-exchange-transfusion-series.html
Thank you very much for the info and your willingness to share.
As I always say… Sharing is caring..
Good work…. please forward us more links if available where people share like you.