Biopsy is a piece of tissue or whole organ removed from body for histological studies. They are removed on the purpose of diagnosis of disease or prognosis of treatments. Meanwhile, the extend of disease and the second pathology of disease could be able to detect by examination biopsies. The biopsy is also used to match the organ tissue prior to transplantation (Example Renal biopsy).
Basically, biopsies can be divided in to 07 groups on the basis of method of removal of tissue form the body .
- Needle biopsy
- Punch biopsy
- Incisional biopsy
- Excisional biopsy
- Currettage biopsy
- Extracting tissue piece by piece
- Endoscopic biopsy
Prior to removal of tissue, the most appropriate type of biopsy going to be made should be determined. This depends on varieties of factors.
- Tissue to be sampled.
- how suspicious the abnormality appears.
- Size, shape and other characteristic of abnormalities
- The location of abnormalities
- Number of abnormalities
1. Needle Biopsy
A needle is inserted through the skin to the suspicious area and cells are extracted. The needle biopsy includes Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA), vacuum assist biopsy and core needle biopsy.
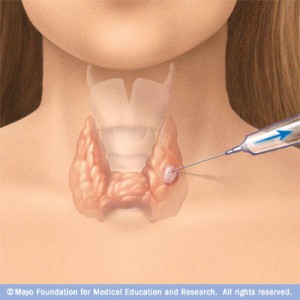
A long thin needle is inserted to the suspicious area and fluid is collected into a syringe. This fluid is sent to the cytology laboratory for cellular studies. (FNA Thyroid gland)
- Vacuum Assist Biopsy
A vacuum pressure is used to collect tissue through a specially designed hollow needle. This procedure facilitates to collect multiple or large samples from the same biopsy site without having to insert the needle more than once. (Example : Breast biopsy)
- Core Needle Biopsy
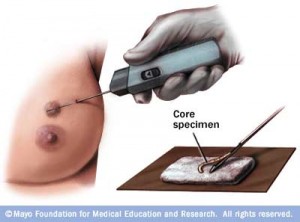 Core needle biopsy is performed by inserting a hollow core needle through the skin to the lesion. This needle is larger than the one used in fine needle biopsy (gauge 16,14 or 11) and it has been designed with a cutting tip to extract a column or cylinder shaped of tissue from the abnormality. The core needle biopsy is performed when the fine needle biopsy didn’t provide a definitive diagnosis. (Example : Trephine biopsy)
Core needle biopsy is performed by inserting a hollow core needle through the skin to the lesion. This needle is larger than the one used in fine needle biopsy (gauge 16,14 or 11) and it has been designed with a cutting tip to extract a column or cylinder shaped of tissue from the abnormality. The core needle biopsy is performed when the fine needle biopsy didn’t provide a definitive diagnosis. (Example : Trephine biopsy)
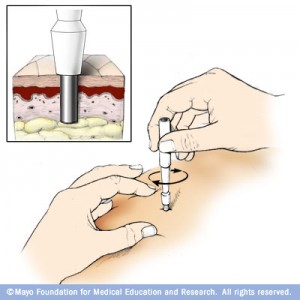
A punch or circular tool is used to extract about 6 mm deep skin layers. This technique is usually used by dermatologists. The punch biopsy is made on exposed areas especially oral mucosa. (Example : Skin biopsy, Rectum biopsy and Oral biopsy)
3. Incisional Biopsy
A scalpel is used to remove a small piece of tissue from large lesion. Incisional biopsy may be used for soft tissues. (Example : Biopsy from Tumors).
4. Excisional Biopsy
The entire lesion is removed from the body.
5. Currettage Biopsy
Removal of piece of tissue by scraping. (endometrial curretings)
6. Extracting Tissue piece by piece
Example : Transurethral Reaction of the Prostate (TURP)
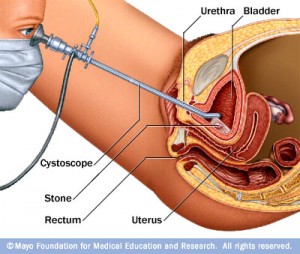
Endoscope is a fine flexible tube with a camera used to view the inside of the body either through a natural body orifice or a small surgical incision. The endoscope used to visualize the different parts of body is named in different names.
- gastrointestinal tract – Alimentary tract endoscope
- Urinary bladder – Cystoscope
- Abdominal cavity – Laparoscope
- Joint cavity – Arthroscope
- Mid point of chest – Mediastinoscope
- Respiratory Tract – laryngoscope or Bronchoscope
The endoscope can visualize the abnormal area on the lining of the organ and pinch off a tiny piece of tissue with forceps attached to a long cable that runs inside the endoscope.
Photo credits: Myoclinic (1998), ” Types of biopsy Procedures used to diagnose Cancer”, available on: www.myoclinic.com/health/biopsy/CA00083
Thanx. Good info
thanks for ur information ~~ it help me in my assignment